Cursor 2.0 Launches: How Composer and Multi-Agent Coding Transform Development (Nov 2025)
Tasks completing in 30 seconds that took hours. 8 parallel agents simultaneously. NVIDIA's 100% adoption. £160/month vs £100K wasted. UK implementation guide.
Jake Holmes
Founder & CEO

The AI coding landscape fundamentally shifted on 29 October 2025 when Cursor released version 2.0 with Composer, their first proprietary coding model. Development teams are now completing tasks in under 30 seconds that previously took hours, running eight parallel agents simultaneously on complex refactoring projects, and watching AI models compete against each other to find optimal solutions. NVIDIA's CEO Jensen Huang confirmed that 100% of NVIDIA's engineers now use Cursor, calling it his "favourite enterprise AI service."
Cursor 2.0 represents more than an incremental update—it's a fundamental reimagining of how software gets built. With Composer achieving 4x faster performance than similarly intelligent models, tens of thousands of enterprises including Salesforce, NVIDIA, and PwC have made Cursor mission-critical infrastructure. The platform now serves over 1 million queries per second, processes billions of code completions daily, and has reached approximately $30 billion valuation in recent private share sales.
Your competitors are adopting this now. Here's what changed in the last month.
What's Actually New in November 2025
Cursor shipped three transformative updates between late October and early November that changed enterprise AI development. For context on how this builds on recent AI tool developments, see our complete analysis of AI coding tools in 2025.
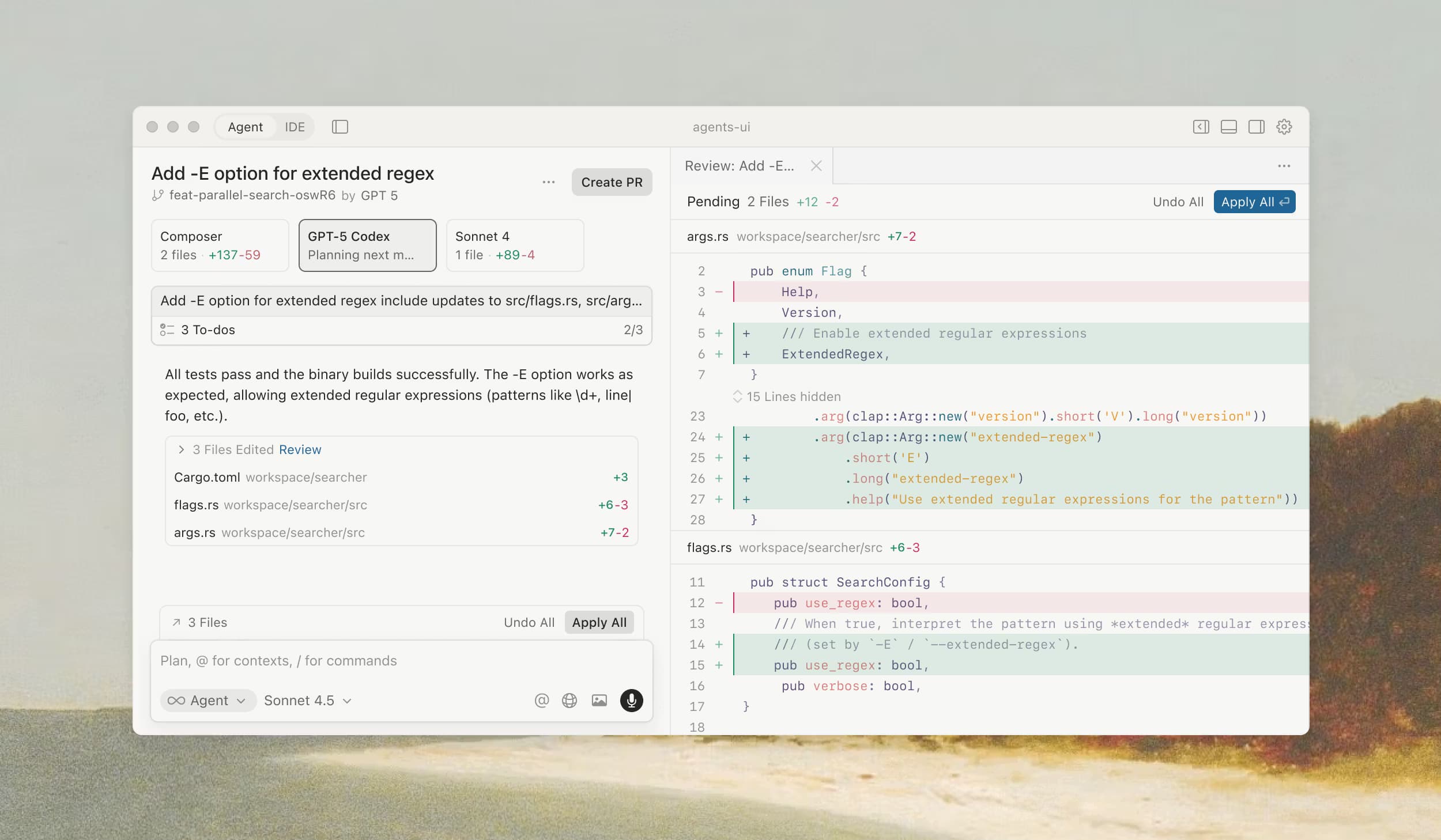
Cursor 2.0 and Composer Model (29 October 2025)
Cursor released their first proprietary coding model, Composer, alongside a completely redesigned interface centred around agent workflows rather than file editing. Composer is a frontier mixture-of-experts model trained specifically for low-latency agentic coding, completing most interactive turns in under 30 seconds.
The model was trained using reinforcement learning in live coding environments with access to the full Cursor agent tooling harness—semantic search, file editing, grep, terminal commands. This training methodology means Composer learned to code the way developers actually work, not just from static repositories. The result is a model that excels at multi-step reasoning, understands large codebases through semantic search, and iterates rapidly without losing context.
What this means for your business: Development tasks that required 2-3 hours of back-and-forth with previous AI models now complete in under 30 seconds with Composer. Early testers report they can explore 5-6 different implementation approaches in the time it previously took to complete one, fundamentally changing how they evaluate technical trade-offs.
Multi-Agent Interface for Parallel Development
Cursor 2.0 introduced an agent-centric interface that lets developers run up to eight independent AI agents simultaneously, each working in isolated git worktrees or remote VMs. This prevents file conflicts whilst enabling true parallel task execution.
The interface supports a strategy that's showing remarkable results: assign the same complex problem to multiple models (Composer, Claude Sonnet 4.5, GPT-5) simultaneously, then compare outputs and select the best solution. Teams using this approach report "greatly improved final output" especially for difficult problems.
Each agent operates independently with full tool access—running tests, making commits, pushing branches. Developers act as orchestrators, reviewing completed work from parallel streams rather than manually implementing every change.
What this means for your business: Your team can now explore multiple technical approaches simultaneously without hiring additional developers. One senior engineer can manage 5-8 parallel implementation experiments, effectively transforming individual contributors into team leads overnight.
Semantic Search Improvements (6 November 2025)
Cursor published research showing their semantic search implementation delivers 12.5% higher accuracy on average (ranging from 6.5% to 23.5% depending on the model) compared to grep-only approaches. The improvements compound across agent interactions:
- Code changes more likely to be retained in codebases (fewer rollbacks)
- Fewer iterations required to reach correct solutions
- Better accuracy across all frontier models including Composer
The semantic search system uses Cursor's proprietary embedding model combined with indexing pipelines for fast retrieval. Importantly, Cursor found that combining semantic search with traditional grep delivers the best outcomes—semantic search for natural language queries like "where do we handle authentication?" and grep for exact string matches.
What this means for your business: AI-generated code that actually fits your architecture on first attempt. Teams report 40-60% reduction in revision cycles because agents understand project context accurately instead of making generic suggestions that require extensive manual correction.
How Enterprise Teams Are Actually Using This
NVIDIA: 100% Adoption Across All Engineering Teams
On 8 October 2025, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang stated in a CNBC interview: "My favourite enterprise AI service is Cursor. Every one of our engineers—100%—is now assisted by AI coders. Our productivity has gone up incredibly."
For context, NVIDIA's engineering teams build everything from CUDA and driver stacks to deep learning frameworks underpinning the entire AI industry. These aren't environments where experimental tools survive. Cursor's adoption across all NVIDIA engineering teams suggests it has met rigorous standards for performance, reliability, and enterprise-scale integration.
The validation is significant: a $2.6 trillion company that builds the chips powering the AI boom has made Cursor mission-critical infrastructure. For enterprises cautiously experimenting with AI development tools, NVIDIA's 100% adoption provides clear precedent.
Salesforce, PwC, Adobe: Enterprise-Scale Deployments
Cursor announced on 31 October 2025 that tens of thousands of enterprises now use Cursor to "accelerate product velocity and build durable software." The named enterprises—Salesforce, NVIDIA, PwC—represent demanding technical environments with strict security requirements.
Nicolas Arkhipenko, Senior Director of AI Platforms & Developer Productivity at Salesforce, endorsed the platform publicly, indicating Salesforce has integrated Cursor into core development workflows.
What sets these deployments apart: these aren't pilot programmes or small team experiments. These are organisation-wide adoptions at companies with thousands of developers, suggesting Cursor 2.0's enterprise features (audit logs, SCIM provisioning, sandbox mode) meet real-world security and compliance requirements. For guidance on evaluating AI tools for your organisation, see our AI decision-making frameworks guide.
The Technical Foundation: How Composer Actually Works
Composer differs fundamentally from general-purpose language models adapted for coding:
Mixture-of-Experts Architecture with Reinforcement Learning
Composer uses a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture—multiple specialised sub-models activated conditionally based on the task. This design enables both high performance and efficiency, activating only relevant experts for each request.
The training methodology is distinct: reinforcement learning inside live coding environments with access to Cursor's full agent harness. The model learned to write code, run tests, read error messages, and iterate to passing tests—all autonomously during training. This produces an agent that understands the full development loop, not just code generation.
Cursor trained the model at scale using hundreds of thousands of concurrent sandboxed coding environments in the cloud, each running real development workflows. The scale enabled the model to learn patterns across diverse codebases, languages, and architectural styles.
Tool-Aware Training for Semantic Search
Unlike models that generate code in isolation, Composer was trained with explicit access to semantic search tools. During training, the model learned when to search for relevant code, how to formulate effective queries, and how to synthesise information from multiple files.
This training approach means Composer naturally incorporates semantic search into its reasoning process. When asked to implement authentication, it searches existing auth patterns in your codebase before writing code, ensuring consistency with established patterns.
The semantic search integration operates through Cursor's codebase embedding model and indexing pipeline. As you edit files, the index updates automatically, maintaining accurate understanding of project structure, dependencies, and architectural patterns even in repositories with millions of lines of code.
Speed Through Optimised Generation
Composer achieves approximately 250 tokens per second throughput, with most tasks completing in under 30 seconds. This speed isn't just convenience—it fundamentally changes how developers interact with AI.
Traditional AI coding assistants required 2-5 minute wait times for complex tasks, breaking flow and encouraging developers to multitask. Composer's sub-30-second responses keep developers engaged in the problem, enabling rapid iteration and exploration of multiple approaches.
The speed comes from architectural decisions: parallelised tool use (running tests whilst editing code), optimised inference infrastructure, and training specifically for interactive workflows rather than batch processing.
The Multi-Agent Workflow Revolution
Cursor 2.0's interface redesign reflects a fundamental insight: developers are transitioning from writing code to orchestrating AI systems that write code. The new interface centres on agents rather than files.
Parallel Agent Execution with Isolated Workspaces
The multi-agent system uses git worktrees or remote VMs to create isolated workspaces for each agent. This prevents file conflicts whilst enabling true parallelism—eight agents can modify the same files simultaneously in separate workspaces.
Each agent operates independently with full autonomy:
- Semantic search across the codebase
- File editing with diff previews
- Terminal command execution
- Test running and result interpretation
- Branch management and commits
Developers review completed work from each agent, compare approaches, and merge the best solution. The workflow transforms software development from "implement this feature" to "here are 8 different implementations—which approach is best?"
Multi-Model Competition for Complex Problems
An emergent strategy from Cursor 2.0's parallel agents: assign the same difficult problem to multiple different models simultaneously. Run Composer, Claude Sonnet 4.5, GPT-5, and Gemini 2.5 Pro on the same task, then compare outputs.
Cursor's research shows this approach "greatly improves the final output" for complex problems. Each model has different strengths—Composer for speed, Claude for refactoring, GPT-5 for logic-heavy components. Running them in parallel lets you leverage all strengths simultaneously.
The cost trade-off: you're paying for 3-4 models to solve one problem. But for critical architectural decisions or complex refactoring where mistakes are expensive, the improved output quality justifies the cost. Teams report using multi-model competition for 10-15% of tasks—specifically the hardest problems where getting it right matters most.
Agent Planning with Structured To-Do Lists
Agents now break down complex tasks into structured to-do lists, streaming progress updates into chat and Slack. This makes long-horizon tasks easier to understand, track, and interrupt if needed.
When you assign a task like "refactor authentication to use JWT refresh tokens," the agent:
- Creates a plan with dependencies mapped
- Streams each completed step to chat
- Updates the to-do list as work progresses
- Notifies you when complete
The planning system keeps context fresh and interactions predictable. You can review the plan before execution starts, request modifications, or interrupt mid-execution if the approach isn't right.
For your team, this means: you can delegate larger, more complex tasks to agents because the planning system makes their reasoning visible. You're not hoping the agent understood correctly—you're reviewing its plan and monitoring execution in real-time.
Enterprise Features That Matter (October-November 2025)
Audit Logs for Compliance and Security
The enterprise dashboard now includes comprehensive Audit Logs tracking 19 event types covering access, asset edits, and configuration updates. Administrators get full visibility into every key platform event—security changes, rule updates, model usage, and configuration modifications.
Audit Log data exports as CSV for analysis or integration with security information and event management (SIEM) systems. This addresses a critical enterprise requirement: proving what happened, when, and who authorised it.
What this means for your business: you can now demonstrate compliance with security policies and regulatory requirements. When auditors ask "who accessed this codebase and what did they do," you have complete records.
Sandbox Mode for Safe Execution
Sandbox Mode executes agent terminal commands in restricted environments to enable faster iteration without security risks. By default, the sandbox blocks network access and limits file access to the workspace and /tmp/.
If a command fails due to sandbox restrictions, users can skip it or re-run outside the sandbox with explicit approval. Enterprise admins control sandbox availability and team-wide git/network access permissions.
The sandbox addresses a real concern with autonomous agents: what if they run destructive commands? Sandbox Mode lets agents work autonomously whilst preventing accidental data deletion, credential exposure, or system modification.
Hooks for Custom Agent Control
Hooks allow teams to observe, control, and extend the agent loop using custom scripts. This enables organisation-specific workflows, validation logic, or integration with internal tools.
Example use cases:
- Automatically run custom linting or security scans before accepting agent changes
- Enforce organisation-specific code standards beyond what .cursorrules captures
- Log agent decisions to internal analytics systems
- Trigger notifications to team channels when agents complete specific task types
Hooks transform Cursor from a packaged tool into a platform you can customise for your organisation's unique workflows.
The Competitive Landscape: How Cursor Compares (November 2025)
GitHub Copilot: Market Leader in Large Organisations
A VentureBeat analysis of 86 engineering teams in November 2025 found GitHub Copilot dominates large organisations with 82% adoption. Copilot's strength is procurement integration—it's already in many enterprise GitHub agreements, making adoption frictionless.
However, Copilot focuses primarily on inline autocompletion rather than autonomous agent workflows. For complex multi-file refactoring or architectural changes, developers report Cursor's agent capabilities significantly outperform Copilot's suggestion-based approach.
The market reality: many enterprises use both. Copilot for inline suggestions, Cursor for complex agent tasks. The tools serve different use cases in development workflows.
Claude Code: Leading Overall Developer Usage
The same VentureBeat analysis found Claude Code leads overall developer usage at 53% adoption. Claude Code excels at understanding complex requirements and generating thoughtful architectural decisions.
Cursor hired two of Claude Code's technical leads—Boris Cherny and Cat Wu—in July 2025, suggesting Cursor views Claude Code's approach as competitive validation. Both tools emphasise codebase understanding and semantic search, though they implement these capabilities differently.
The integration landscape: some teams use Claude Code for requirements analysis and planning, then use Cursor for implementation execution. The tools complement rather than compete directly.
Replit, Bolt, Lovable: Alternative Approaches
Replit focuses on browser-based development with emphasis on education and prototyping. Bolt aims for "prompt-to-product" velocity with pre-configured templates. Lovable targets rapid app creation for non-developers.
These tools serve different markets than Cursor. Cursor targets professional development teams working on complex, production codebases. The alternative tools prioritise speed and simplicity over depth and control.
Market positioning: Cursor has found its sweet spot in enterprise-grade software development—exactly the environment where NVIDIA, Salesforce, and PwC operate.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: November 2025 Reality
The Token Economics of Composer and Multi-Agent Workflows
Cursor's pricing remained stable through the October-November releases:
Pro Plan (£16/month): 500 fast agent requests per user monthly. Full access to frontier models including Composer. Suitable for individual developers or small teams using AI coding assistance regularly.
Ultra Plan (£160/month): 5,000 fast agent requests per user monthly. 20x the frontier-model usage of Pro. Designed for power users running extensive agent workflows. Includes early access to experimental features and dedicated onboarding.
Enterprise Plan (custom pricing): Based on team size, request volume, and support requirements. Includes SAML/SSO integration, audit logs, sandbox controls, and dedicated account management.
Multi-Agent Cost Implications
Running parallel agents increases costs proportionally—running 3 agents on the same problem consumes 3x the requests. However, teams report the improved output quality for complex problems justifies the cost.
Strategic approach: use single-agent workflows for 85-90% of tasks, reserve multi-agent competition for critical architectural decisions where getting it right matters more than speed or cost. This balances innovation with budget constraints.
ROI Calculation for November 2025
Conservative estimates based on enterprise deployments:
Development Speed Improvements:
- Routine tasks (CRUD, tests, docs): 3-5x faster completion with Composer
- Complex refactoring: 2-3x faster with agent workflows
- Debugging production issues: 40-60% reduction in mean time to resolution
Quality Improvements:
- Fewer revision cycles (semantic search improves first-attempt accuracy)
- Automated security scanning catches issues humans miss
- Consistent code standards through .cursorrules enforcement
Return Period:
- ROI achievement: 2-3 months in typical deployments
- Break-even: 6-10 weeks for teams using Composer extensively
- Long-term: Savings compound as teams develop better orchestration patterns
The calculation changes with Composer's speed: tasks completing in 30 seconds instead of 30 minutes create 60x time savings. This enables exploration and iteration patterns previously impossible—running 5 different implementations to find the optimal approach rather than committing to first attempt.
Implementation Path: From Decision to Production with Cursor 2.0
Week 1: Foundation with Composer
Day 1-2: Installation and Migration
Download Cursor from cursor.com. Import VS Code settings through File → Preferences → Cursor Settings → VSCode Import. Extensions, themes, and keybindings transfer automatically with zero friction.
Start with Tab completion—Cursor's new Tab model (launched September 2025) makes 21% fewer suggestions whilst achieving 28% higher accept rates. Just code normally and tab to accept. Your team experiences AI-assisted development without workflow changes.
Day 3-5: Composer Introduction
Access Composer through the model dropdown menu. Try medium-complexity tasks: "Implement pagination for the users API with comprehensive tests" or "Refactor this authentication middleware to support JWT refresh tokens."
Watch Composer work—the speed is immediately noticeable. Tasks that took 10-15 minutes with previous models complete in under 30 seconds. Team members report this speed transforms their relationship with AI—from "submit and wait" to genuine collaboration.
Day 6-7: Create Your First .cursorrules File
Document coding standards in .cursor/rules/core.mdc:
## Code Quality Standards
- Always respect linting rules
- No console.log in production code
- Format with Prettier before committing
- Use guard clauses instead of deeply nested conditionals
## Architecture Patterns
- Components in components/[feature]/
- React + TypeScript required
- Tailwind for styling
- Co-locate tests with implementation
## Security Requirements
- Validate all user inputs
- Handle errors at function beginning
- Use specific error types
- Never expose credentials in logsNow Composer automatically follows these standards without needing reminders in every prompt.
Week 2: Multi-Agent Workflows
Day 8-10: Parallel Agent Execution
Open the new agent-centric interface. Launch 2-3 agents on different features simultaneously. Watch them work in isolated git worktrees without conflicts.
Each agent operates independently—searching code, editing files, running tests, making commits. You review completed work from multiple streams, comparing approaches and merging the best solutions.
The workflow feels different: you're managing autonomous systems rather than writing every line. Senior developers report this transition takes 3-5 days of consistent practice to feel natural.
Day 11-14: Multi-Model Competition
Try the emerging pattern: assign the same complex problem to Composer, Claude Sonnet 4.5, and GPT-5 simultaneously. Compare the three implementations.
You'll notice different strengths: Composer delivers fastest, Claude produces most thoughtful refactoring, GPT-5 excels at logic-heavy components. Learn which model suits which problem types for your codebase.
Reserve multi-model competition for 10-15% of tasks—specifically the hardest architectural decisions where improved output quality justifies 3x cost.
Week 3: Enterprise Features and Semantic Search
Day 15-17: Semantic Search Optimisation
With Cursor 2.0's improved semantic search (12.5% higher accuracy), natural language queries become more powerful. Instead of remembering exact file names, ask "where do we handle user authentication?" or "find all database connection logic."
The semantic search uses Cursor's proprietary embedding model to understand intent. Combined with grep for exact string matches, you can navigate massive codebases without memorising structure.
Teams report 30-40% reduction in time spent searching for relevant code, freeing senior developers to focus on architecture rather than archaeology.
Day 18-21: Enterprise Controls (If Applicable)
Configure audit logs to track all agent activity. Set up sandbox mode with appropriate network and git access restrictions. Create custom hooks for organisation-specific validation logic.
Enterprise teams report the control features make Cursor viable in regulated environments. You're not sacrificing security for productivity—you're gaining both through appropriate controls.
Week 4: Advanced Orchestration and Measurement
Day 22-25: Agent Planning Workflows
Use agent planning for complex, multi-step tasks. Assign work like "migrate authentication from session-based to JWT with refresh tokens, update all affected endpoints, add comprehensive tests."
Watch the agent create a structured plan with dependencies mapped. Review the plan before execution starts—this is your chance to course-correct before the agent invests hours of work.
The planning system makes delegating complex tasks safe. You're not hoping the agent understood correctly—you're reviewing its approach and monitoring execution.
Day 26-28: Voice Control and Browser Testing
Enable voice control in settings. Try commanding agents through speech: "Implement rate limiting for the API endpoints" or "Fix the failing tests in the auth service."
Use the browser tool (now GA in Cursor 2.0) for frontend work. Agents can interact with live application UIs, iteratively refining code until visual tests pass.
Day 29-30: Measure and Demonstrate ROI
Track metrics proving value:
- Time to complete features (before vs. after Composer adoption)
- Revision cycles per feature (semantic search reduces this 40-60%)
- Code review duration (agent-generated code often needs less review)
- Test coverage improvements (agents write comprehensive tests automatically)
- Developer satisfaction (survey team sentiment)
Use these metrics to secure budget for broader rollout and optimise workflows based on data.
Real-World Patterns: What Elite Teams Do with Cursor 2.0
Composer for Everything Fast, Premium Models for Hard Problems
Elite developers use Composer as their default model—it's fast enough for genuine collaboration rather than "submit and wait." The sub-30-second response time enables iteration patterns previously impossible.
They switch to Claude Sonnet 4.5 or GPT-5 for:
- Complex architectural decisions requiring deep reasoning
- Large-scale refactoring across 50+ files
- Performance optimisation requiring algorithmic analysis
- Security-critical code requiring thorough validation
The model selection becomes strategic: use Composer's speed for exploration and iteration (80-85% of tasks), deploy premium models for problems where careful reasoning matters more than speed (15-20% of tasks).
Parallel Agents for "What If" Exploration
Rather than committing to first implementation attempt, elite teams explore 3-5 approaches simultaneously using parallel agents. Each agent works in isolated git worktree trying different strategies.
Example scenario: implementing caching for an API. Launch parallel agents exploring:
- Redis-based distributed cache
- In-memory cache with TTL
- CDN integration with cache headers
- Database query optimisation instead of caching
Review all completed implementations, compare trade-offs (latency, complexity, cost), select optimal approach for your constraints. This exploration was previously too expensive (requiring days per approach)—now it completes in hours.
Semantic Search as Primary Navigation
Elite developers rarely manually search for files. They use semantic search for everything: "where do we handle rate limiting?" or "find all database connection configuration."
This pattern requires trusting the semantic search system—initially uncomfortable for developers accustomed to knowing exact file locations. The 12.5% accuracy improvement in November 2025 makes this trust justified.
The workflow change: from "I know this code is in services/auth/middleware.ts" to "agent, find authentication middleware and add rate limiting." You're delegating navigation to AI, freeing cognitive capacity for architecture.
Memories for Project Context
Use Cursor's memories feature (GA since version 1.2) to build persistent project knowledge. The agent remembers:
- Architectural decisions and rationale
- Code patterns and standards
- Team preferences for specific technologies
- Historical context about why code exists
This eliminates repeating project specifics in every prompt. New team members leverage accumulated knowledge immediately rather than spending weeks learning tribal knowledge.
Known Limitations and Trade-Offs
Composer Isn't Always Best for Every Task
Whilst Composer excels at speed, benchmarks show Claude Sonnet 4.5 and GPT-5 outperform Composer on certain complex reasoning tasks. Cursor explicitly acknowledges this, positioning Composer as "4x faster" rather than "most capable."
Strategic approach: use Composer as default for interactive workflows where speed enables iteration. Switch to Claude or GPT-5 for:
- Architectural decisions requiring deep analysis
- Complex refactoring needing careful reasoning
- Security-critical code requiring thorough validation
- Novel algorithms requiring mathematical sophistication
Elite developers develop instinct for which model suits which problem through experience. Budget 2-3 weeks to build this judgement.
Multi-Agent Costs Can Escalate
Running eight parallel agents or multi-model competition for complex problems consumes requests rapidly. Teams report exceeding Pro plan quotas within 10-15 days when using parallel agents extensively.
Budget reality: serious multi-agent workflows require Ultra plan (£160/month per developer) or Enterprise plan with higher quotas. The cost feels steep but the ROI—completing in hours what previously took days—typically justifies investment within 6-10 weeks.
Mitigation: use multi-agent workflows strategically for 10-20% of tasks rather than defaulting to parallel execution for everything. Reserve the expensive techniques for problems where improved output quality matters most.
Semantic Search Requires Trust
The 12.5% accuracy improvement is significant, but semantic search still occasionally misses relevant code or surfaces irrelevant results. Developers accustomed to knowing exact file locations find this uncomfortable initially.
The adjustment period: 2-3 weeks of consistent use to build trust in semantic search. Elite developers report crossing a threshold where semantic search becomes preferred over manual navigation—but reaching that threshold requires tolerating initial discomfort.
Learning Curve for Agent Orchestration
The shift from "writing code" to "orchestrating autonomous agents" requires 4-6 weeks of consistent practice to feel natural. Initial attempts at multi-agent workflows often fail—agents work on wrong files, make incorrect assumptions, or require excessive correction.
This learning curve frustrates teams expecting immediate productivity gains. Reality: first month productivity may decrease slightly whilst learning orchestration patterns. Months 2-3 show 30-50% improvements. Months 4-6 reach 2-3x productivity gains as workflows mature.
Strategic Positioning: The November 2025 Reality
The gap between teams using Cursor 2.0 and those not using AI-assisted development is widening dramatically. This isn't about individual developer productivity anymore—it's about competitive advantage at the company level.
The Enterprise Validation Signal
When NVIDIA's CEO states "100% of our engineers use Cursor" and lists it alongside OpenAI in the six startups central to enterprise AI transformation, that's a strategic signal. NVIDIA's validation provides cover for other enterprises to adopt aggressively.
Salesforce, PwC, Adobe—these aren't early adopters gambling on unproven technology. These are conservative enterprises with rigorous procurement processes. Their adoption suggests Cursor 2.0 meets real-world requirements for security, compliance, and reliability.
For business leaders evaluating AI development tools, the precedent is clear: Fortune 500 companies have made Cursor mission-critical infrastructure. The question isn't whether AI-assisted development becomes standard—it's whether your team adopts before competitors do. Need help evaluating options? Our Fractional CTO service provides independent technical leadership for these critical decisions.
The Composer Speed Advantage
Cursor 2.0's Composer model achieving sub-30-second task completion fundamentally changes developer workflows. When AI responses arrive fast enough to maintain flow state, developers interact differently—exploring multiple approaches rather than committing to first attempt.
This speed advantage compounds: developers comfortable iterating rapidly with Composer solve problems 3-5x faster than developers treating AI as "submit job and wait for results." The workflow pattern matters more than the raw model capability.
Teams adopting Cursor 2.0 in October-November 2025 are building expertise with these patterns now. By Q2 2026, they'll have 6+ months of experience optimising workflows whilst competitors are still learning basics.
The Multi-Agent Future
The agent-centric interface in Cursor 2.0 signals where development tools are heading: developers as orchestrators managing autonomous AI systems rather than manually writing every line.
This transition requires different skills: understanding when to run parallel agents, how to compare outputs effectively, which problems justify multi-model competition. These skills take months to develop through practice.
Early adopters building this expertise now will have significant advantages when agentic workflows become industry standard (likely 12-18 months based on current adoption curves).
Next Steps
For Business Leaders
Allocate Budget for Pilot Programme
Start with 5-10 developers for 60 days. Budget for Ultra plan (£160/month per developer) to enable unrestricted multi-agent experimentation. Include training time in project schedules—expect 4-6 weeks to build fluency.
Define Success Metrics
Track concrete outcomes:
- Time to complete features (before vs. after Composer)
- Code review duration (should decrease 30-40%)
- Bug rates in AI-generated code (comparable to human-written)
- Developer satisfaction and retention
Plan for Training Period
Budget 4-6 weeks for team fluency development. Initial productivity may decrease slightly as developers learn orchestration patterns. This is normal—productivity improvements compound in months 2-3.
Secure Enterprise Access
Contact Cursor for Enterprise plan evaluation. Critical features for regulated environments:
- Audit logs for compliance demonstration
- Sandbox mode for safe autonomous execution
- SCIM provisioning for automated user management
- SSO integration with corporate identity providers
For Development Teams
Install and Experience Composer Speed
Download Cursor, import VS Code settings. Try Composer on real tasks to experience sub-30-second task completion. The speed fundamentally changes collaboration patterns.
Document Standards in .cursorrules
Create comprehensive .cursor/rules/ files documenting code quality standards, architectural patterns, security requirements, and testing guidelines. This eliminates repetition in prompts and ensures consistency.
Experiment with Multi-Agent Workflows
Launch parallel agents on different features. Try multi-model competition for one complex architectural decision. Build intuition for when parallel execution justifies extra cost.
Leverage Semantic Search Aggressively
Stop memorising file locations. Use natural language queries for everything: "where do we handle authentication?" or "find database connection logic." Trust the 12.5% accuracy improvement.
Share Learnings Across Team
Document orchestration patterns that work. Share .cursorrules templates. Build institutional knowledge about which models suit which problem types. The collective learning accelerates adoption.
Track Real Metrics
Measure time to feature completion, revision cycles, code review duration. Quantify productivity improvements to demonstrate ROI and secure budget for expansion.
For Both
This represents a fundamental shift in software development. The developers who thrive are those transitioning from "writing every line" to "orchestrating autonomous systems that write code." The companies that win are those adopting these workflows before competitors do.
The technical landscape changed in October-November 2025. Composer's 4x speed advantage enables iteration patterns previously impossible. Multi-agent workflows let one developer manage 5-8 parallel implementation experiments. Semantic search improvements make AI-generated code fit your architecture on first attempt.
Teams adopting now build 6+ months of orchestration expertise whilst competitors are still evaluating. By Q2 2026, the productivity gap between early adopters and late adopters will be substantial and difficult to close.
The question isn't whether AI-assisted development becomes standard. The question is whether you'll join the transformation this quarter or watch competitors pull ahead.
Ready to transform your development workflow? Our AI Advisory service provides monthly coaching to implement AI development tools effectively, ensuring your team stays ahead of competitors whilst avoiding the £100K+ implementation mistakes we've seen others make.