AI Watermarks: The Invisible Markers in Your Business Content and What They Mean
Every piece of AI-generated text may contain invisible Unicode characters that identify it as machine-written. Here's what UK businesses need to know about AI watermarks, detection tools, and managing AI-assisted content.
Jake Holmes
Founder & CEO
Updated: January 2026 | Reading Time: 10 minutes
If your business uses ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini to draft emails, reports, or marketing copy, there's something you might not know: that content may contain invisible markers that identify it as AI-generated. These "watermarks" are embedded in ways humans can't see but detection tools can find.
For UK businesses using AI as a productivity tool, this raises practical questions about content authenticity, privacy, and how AI-generated text behaves when copied between applications.
What are AI watermarks and how do they work?
AI watermarks are subtle patterns embedded in generated content that allow later identification of AI authorship. They come in two main forms:
1. Statistical watermarks
These work by influencing which words the AI chooses. Instead of randomly selecting from equally likely options, the model follows a pattern that's invisible to readers but detectable with the right tools. OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic have all explored this approach.
Research from the University of Maryland demonstrated that these patterns survive editing, translation, and paraphrasing surprisingly well. Even substantial rewrites often preserve enough of the statistical signature to flag content as AI-generated.
2. Character-level watermarks
These insert invisible Unicode characters into the text itself. Common examples include:
- Zero-width spaces (U+200B) – Characters that take no visible space
- Zero-width joiners (U+200D) – Used in complex scripts but invisible in English
- Soft hyphens (U+00AD) – Suggest word break points but display nothing
- Non-breaking spaces (U+00A0) – Appear identical to normal spaces
These characters carry no meaning to readers but create a fingerprint that detection systems can identify.
Why do AI companies add watermarks?
The motivations are practical:
Academic integrity: Universities want to identify AI-generated essays. According to 2024 research, over 60% of UK universities now use AI detection tools as part of assessment review.
Content provenance: As AI-generated content becomes harder to distinguish from human writing, watermarks help platforms and publishers verify origin. This matters for news organisations, social media platforms, and anywhere authenticity affects trust.
Regulatory preparation: The EU AI Act and similar regulations may eventually require disclosure of AI-generated content. Watermarks provide a technical mechanism for compliance.
Research and safety: Tracking how AI content spreads helps researchers understand misuse patterns and improve safety measures.
What does this mean for business use?
For most legitimate business applications, AI watermarks present no problem. Using AI to draft internal documents, brainstorm ideas, or accelerate routine writing is perfectly reasonable.
But there are edge cases worth considering:
Content that claims sole authorship
If you're publishing thought leadership, academic papers, or creative work that presents as entirely human-written, invisible markers could create awkward situations if discovered. Many professionals now add disclosure like "drafted with AI assistance" to avoid this entirely.
Cross-application formatting issues
Invisible Unicode characters don't always behave predictably when content moves between systems. You might notice:
- Extra spacing that appears in certain fonts or applications
- Word counts that don't match what you see on screen
- Search functions that miss text because of hidden characters
- Formatting inconsistencies when pasting into CRMs, email tools, or publishing platforms
Client deliverables
Some clients, particularly in legal, financial, or regulated industries, may have policies about AI-generated content. Invisible markers could surface during their review processes.
How to check for invisible characters
If you're curious whether your AI-generated content contains invisible markers, there are simple ways to check:
Character count comparison: Paste text into a tool that shows character counts. If the count exceeds what you'd expect from visible text, invisible characters are present.
Hex editors: These show the actual bytes in a file, revealing any hidden Unicode characters.
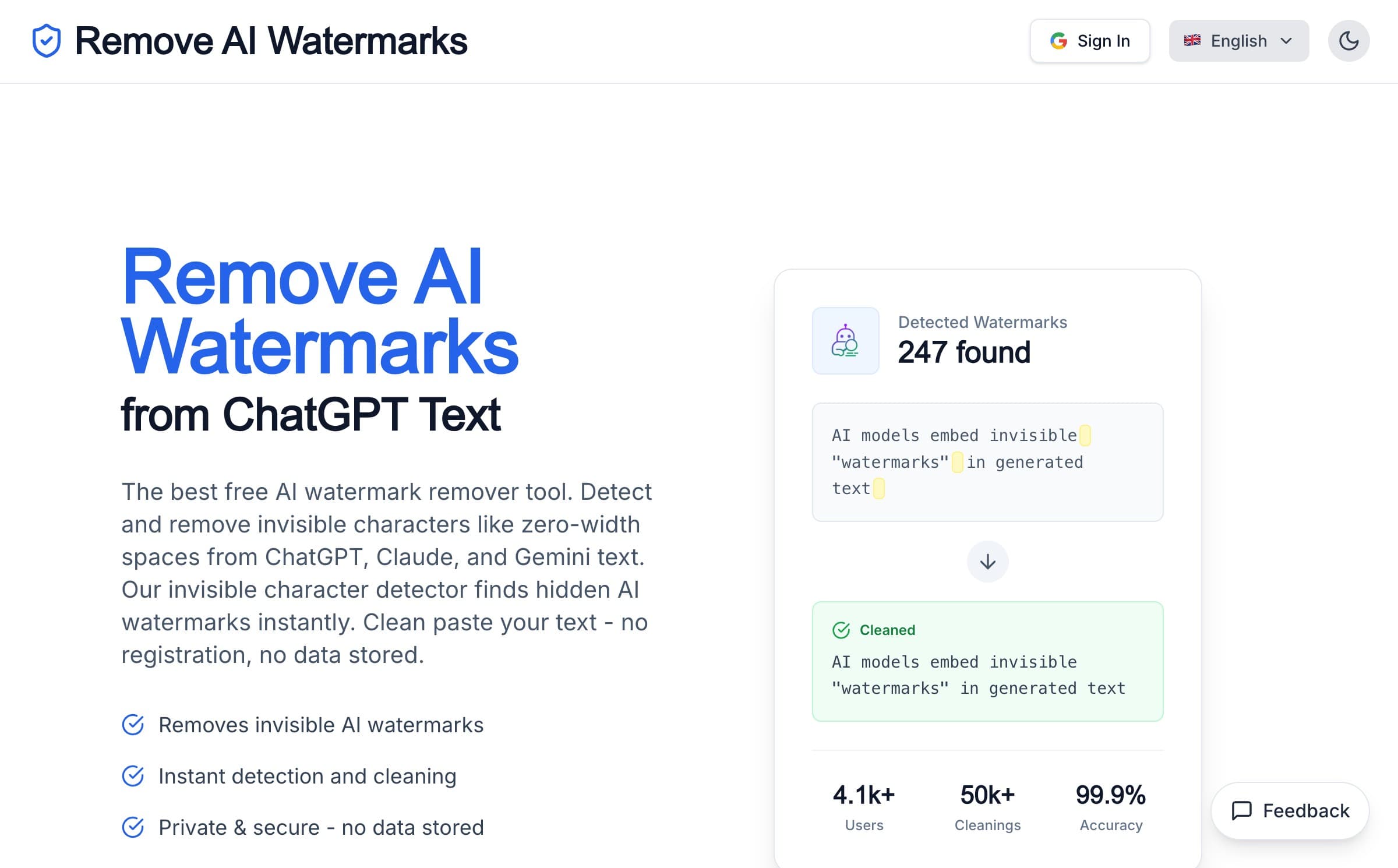
Specialised detection tools: Several online tools specifically identify AI watermarks and invisible characters. We built GPT Watermark Remover to handle this—it detects and removes invisible Unicode markers whilst preserving your visible content, all processed locally in your browser for privacy.
The detection arms race
AI watermarking exists in tension with detection evasion. As watermarking techniques improve, so do methods to remove or circumvent them. This creates a dynamic where:
Watermarks are imperfect: No watermarking system is completely robust. Sufficient rewriting, paraphrasing through another AI, or manual editing can often remove statistical patterns.
False positives occur: Detection tools sometimes flag human-written text as AI-generated, particularly for technical or formulaic writing. This has caused problems in academic settings where students are wrongly accused.
The goal isn't perfection: Watermarks don't need to be unbreakable to be useful. They raise the effort required to misuse AI content, which deters casual abuse even if determined actors can work around them.
Current state of major AI providers
Here's what we know about watermarking from the main AI providers:
OpenAI (ChatGPT): Has developed text watermarking technology but has been cautious about deploying it publicly. Their approach focuses on statistical patterns rather than visible markers.
Google (Gemini): Implements SynthID for images and has explored text watermarking. Their focus has been on audio and visual content where detection is more challenging.
Anthropic (Claude): Has discussed watermarking as part of their safety research but emphasises transparency and disclosure over technical detection.
All major providers continue developing watermarking capabilities, partly in response to regulatory expectations and partly as a safety measure.
Practical recommendations for UK businesses
Based on how AI watermarking actually works, here's sensible guidance:
1. Use disclosure when appropriate
The simplest solution to any watermarking concern is transparency. Adding "drafted with AI assistance" or similar disclosures eliminates questions about authenticity. Many professionals find this actually builds trust rather than undermining it.
2. Clean content for technical consistency
If you're experiencing formatting issues or want clean text for publishing systems, running content through a tool like GPT Watermark Remover ensures no invisible characters cause problems downstream.
3. Understand your industry's expectations
Regulated industries have different standards. Legal and financial services may require explicit disclosure of AI use. Academic publishing has strict policies. Know what applies to your sector.
4. Treat AI as a tool, not a ghost writer
The most practical approach is viewing AI as a drafting assistant. When you substantially edit, fact-check, and refine AI output, the final content genuinely reflects your input regardless of how it started.
What about detection tools?
AI detection services like GPTZero, Originality.ai, and Turnitin's AI detection claim to identify AI-generated content. Their accuracy varies significantly:
- False positive rates can exceed 10% on human-written text
- Heavily edited AI content often passes as human-written
- Technical and formulaic writing is frequently misclassified
- Non-native English writers face disproportionate false positives
For business purposes, these tools are better suited for internal quality control than definitive judgments about content origin.
The future of AI content verification
Watermarking will likely become more sophisticated and more common. Regulatory frameworks like the EU AI Act may require verifiable content provenance for certain use cases. Meanwhile, cryptographic approaches and content credentials (like those from the Content Authenticity Initiative) offer alternatives to embedded watermarks.
For now, the practical impact on most business users is minimal. AI watermarks are an interesting technical development worth understanding, but they shouldn't change how you use AI tools for legitimate productivity purposes.
Key Takeaways
- AI watermarks are invisible markers embedded in generated text, using either statistical patterns or hidden Unicode characters
- Major AI providers are developing and deploying watermarking as a safety and compliance measure
- For most business use, watermarks present no practical issue—transparency about AI assistance is the simplest approach
- Invisible characters can cause formatting problems when copying between applications
- Detection tools exist but have significant accuracy limitations
- Cleaning tools like GPT Watermark Remover can remove invisible markers for technical consistency
Need Help With AI Implementation?
Navigate AI tools and their implications with expert guidance. Grow Fast helps UK businesses (£1-10M revenue) implement AI solutions that deliver measurable efficiency gains whilst managing practical concerns like content authenticity and compliance.
Our Services:
- AI Audit: One-day assessment identifying where AI tools can save £50K+ annually across your operations
- AI Advisory: Monthly coaching on AI tool selection, implementation, and best practices
- Fractional CTO: Technical leadership to guide your AI strategy and vendor decisions
Book a free 30-minute AI strategy session: https://calendly.com/jake-grow-fast/30min
This guide reflects the state of AI watermarking technology as of January 2026. The field evolves rapidly, and practices may change as new research emerges and regulations develop.


